How are man-made diamonds created? Find out all you need to know right here. Thanks to the powers of science, there's no need to venture down into the earth's core to retrieve the almighty King of the Jewels, the diamond. This can now be safely done in the confines of a laboratory completely conflict-free.
Synthetic, man-made or lab-grown diamonds, while they aren't mined from deep within the earth's crust like a natural diamond, there is little to distinguish the two visually. Unless you are quite the diamond expert, of course. Man-made diamonds have grown in popularity in recent years, largely due to the fact that lab-grown diamonds come in at a lower price point.
Another reason why these diamonds have gone up in popularity is because they are a way that people ensure that their stone has been sourced ethically. In fact, many diamond suppliers will often market their lab-grown stones as conflict-free. Jump to a section below by clicking the links or read on to find out how man-made diamonds are created.
How Are Man Made Diamonds Created Overview:
- How are synthetic diamonds made?
- High pressure, high-temperature diamond growth (HPHT)
- Chemical vapor deposition (CVD)
- HPHT vs CVD: what's better?
Can Diamonds Be Man-Made?
Diamonds can be man-made. There are two types of man-made diamonds out there. One is created through a process known as high pressure, high-temperature diamond growth or HPHT. The other is produced through a process known as chemical vapor deposition or CVD.
The great thing about lab diamonds is that they are also available in a variety of shapes and colours. Like natural diamonds, synthetic diamonds can be subjected to treatments to change their colour, or to improve their face-up appearance and clarity. Many consumers are also choosing lab-grown diamonds today because there's much less environmental impact in the way they're sourced. They are, of course, graded and priced using the Four C's grading system to ensure that they are chemically and physically optimal.
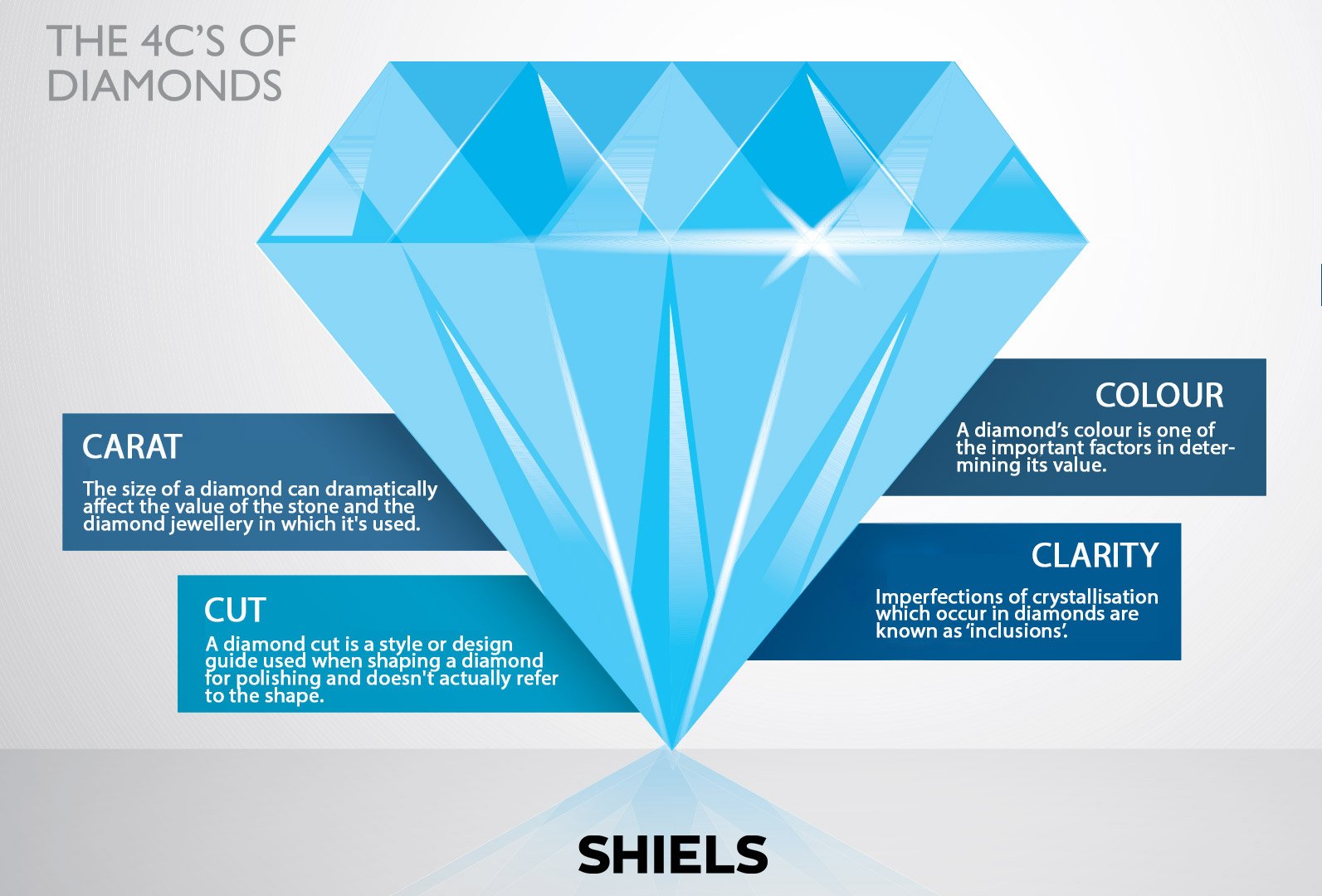
Learn more about the Four Cs of diamonds in our Diamond Buyers Guide.
High Pressure, High-Temperature Diamond Growth (HPHT)
The high pressure, high-temperature process in which lab-grown diamonds are made is designed to mimic the conditions that a natural diamond is produced in. Think about how an incubator can mimic the environment of a mother's womb for a newborn baby or animal. This method involves placing a tiny diamond seed (which is authentically grown through a process known as nucleation) into a piece of carbon.
Following this, using either a belt press, split-sphere (BARS) press or a cubic press, the maker will pressurise the carbon to approximately 680 thousand kilograms per square inch. While this is occurring, the carbon is exposed to temperatures well over 1400 degrees celsius. This pressure and heat begin to melt the diamond, forming a diamond shape over the initial seed. They typically grow outward on the octahedral and cube faces.
Originating in the 1950s, HPHT diamonds were intended to make the diamond industry more lucrative. However, there has been debate as to whether or not this has actually happened. Companies are able to purchase cheaper, less desirable diamonds and put them through the HPHT process to enhance them. While this has resulted in profit, accessibility and a wider selection of diamonds, there are those who detest the process. If you are in the market for diamond jewellery, it is important that you are well informed about the origins of your diamond. This is half the answer to 'how are man made diamonds created,' read on to find out the second way.
Learn more:
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Just as the HPHT process does, the CVD process also requires a small diamond seed. The seed is placed into a sealed chamber where it is filled with carbon-rich gases such as methane or hydrogen and exposed to temperatures of up to 760 degrees celsius.
These gases are then ionised and melted into plasma using technology that is similar to what is used in microwaves. This process breaks down the molecular structure of the gases, allowing carbon to stick to the seed and form a diamond.
They typically grow mainly upward in one direction (a cube face). Additional heat and radiation can be added to the stone following its conception to enhance and alter its colours. You can find a range of different coloured pieces in our white gold lab created diamond ring, lab-created yellow diamond ring and our rose gold lab created diamond ring collections.
Don't be fooled by their name. These diamonds feature exactly the same chemical makeup as mined diamonds. In fact, even a trained jeweller cannot identify the difference. They are often compared to cubic zirconia, however, this is not a comparison that should be entertained because they are completely different. CVD diamonds are made with carbon while cubic zirconias are made from synthetic zirconium dioxide.

HPHT vs CVD: What's better?
HPHT and CVD diamonds do not vary much in terms of composition and value. They do, however, have a few characteristics which can be used to differentiate the two. One of these differentiating factors is the fact that CVD diamonds grow in one direction, while HPHT diamonds can grow in fourteen directions. This not only determines the stone's physical characteristics but it can also be used as a guide to differentiating between natural and man-made diamonds.
HPHT diamonds are often associated with stones that are more brown and yellow in colour while CVD diamonds often tend to be colourless. As the makers have the ability to add nitrogen and boron to the chamber, the CVD process can often produce stones that are yellow or blue in colour. The CVD process is also less costly than HPHT due to the lower temperatures and smaller machinery involved.
Despite these key differences, HPHT and CVD diamonds are both recognised as being high-quality alternatives to the traditional natural diamond. When it comes to diamond jewellery, the choice is really up to you. It typically takes a few weeks to make a lab-grown diamond while a natural diamond spends millions or billions of years in the Earth.

Now you know the answer to 'How are man-made diamonds created,' be sure to learn more about lab-grown diamonds below. Explore Shiels' exquisite range of lab-grown diamond jewellery online and in-store now! We offer a range of lab-grown diamond rings, lab-grown diamond necklaces and lab-grown diamond pendants. We also stock a range of lab-grown diamond earrings to suit every style. Be sure to visit us in store to ask about our stunning man-made diamond collection.